
What is Crossfit
Crossfit (or HIIT – highly-intense interval training) has long and firmly entered the list of the most popular fitness exercises. Everyone knows what CrossFit training looks like. In a nutshell: these are high-intensity power training that alternates between intense exercise and short breaks for rest and recovery.
Crossfit training is based on one of the three options below:
- The amount of load without taking time into account. The exercises and the number of repetitions per 1 circle are set.The circle is executed, followed by a short rest, and is repeated again from the beginning. Circle example: pull-ups – 10 times; push-ups – 20 times; Squats – 30 times. The set exercises are performed, followed by rest, then the exercises are repeated again, rest, etc. – depending on the intensity of the needed workout.
- A certain amount of load is set, which you must try to perform faster than the previous one. Example: pull-ups – 100 times, push-ups – 200 times, squats – 300 times. Based on previous workouts, the time that you anavar results after 2 weeks spend on this volume is already known. It is important to try to fulfill the same volume within a shorter time.
- A fixed time is set, where each workout needs to fulfill an increasing amount of load. Example: the amount of load is determined as a certain number of circles (1 circle: pull-ups – 10, push-ups – 20, squats – 30). Knowing that at the previous workout, for example, 5 laps were completed in 30 minutes, we try to complete more laps in the same 30 minutes.
Each workout routine will vary. But in general, Crossfit training is characterized by tracking your progress.
What exercises are used in Crossfit
Crossfit workouts are made up of various exercises. These exercises are taken from different sports such as gymnastics, athletics, weightlifting, swimming, rowing, etc. There are also a variety of stylized activities taken from competitive games too. This includes tug of war, throwing stones, tossing and turning heavy objects (large car tires), running with weights, and the like.
Within one training session, the load is regulated based on the number of exercises and its duration. During the process, the exercises are often modified to achieve maximum intensity. For example, push-ups are performed in a kneeling position first. After a while, it is then switched to regular push-ups where the legs are in a straight position. So any exercise can be modified as you see fit: Adding weights, changing the starting position, workout with a partner, and so on.
What is the problem of Crossfit
If you expand Crossfit into its component exercises, then there won’t be any issues.
Crossfit is composed of a variety of exercises. Most of which is pretty much reminiscent of the good old physical education (OFP – general physical training) back in the days. These are all wonderful, time-tested exercises that are proven to enhance one’s health.
Progress tracking, competitive exercises, strong teamwork, and the desire to achieve greater heights – these factors are what makes Crossfit fun for athletes and people who want to get fit.

Crossfit marketers have built their concept based on physical fitness. As well as adapting to new surroundings, sticking to the rule of competition, building a global brand, establishing a club of like-minded people, and creating a recognizable style in every aspect of the market (clothes, shoes, equipment, etc.).
At the same time, it is a product of advertising cooperation with the largest sports brand such as Reebok. For a brand as well-known such as this, entertainment and recognition are an element of marketing to increase sales. Reputable sports manufacturers do their own training programs and services to help sell sports goods. Take the Nike NTC app for women, which is a beautifully and visually designed “killer” functional training platform performed by famous sports stars. Or the Nike Running Club running app where you can track your jogging options, as well as tons of other features too.
Let’s talk about the Crossfit and what matters in this ongoing debate. There are two camps – fanatical fans and ardent opponents. We do not relate to either one or the other, because we simply analyze the workout development and understand them from the point of view of training theory. We do our best to apply them in our work without our emotions getting the betterment of us. (We also teach this at seminars to enhance your ability to analyze and understand methods without blindly accepting or rejecting without theoretical justification).
Our attitude to Crossfit is determined by how much it is beneficial for one’s health. We also host various physical training exercises in group classes and also in personal training.
There is no such problem in Crossfit. The problem may lie when doing incorrect Crossfit exercises where there is a possibility of harming oneself. Luckily, this can be avoided if you pay attention to protect yourself in training with minimal accidents.
The challenges encountered in Crossfit: technical disturbances
The Crossfit training methodology increases the likelihood of ignoring the correct exercise technique. This is natural because in the foreground of the exercise is temporary and quantitative rather than qualitative. The need to comply with certain technical guidelines is required. But thousands of videos posted on the internet prove that the technique is secondary to cross-fitters (examples there will be slightly lower executions and repetitions). The fitness advancement made by technology is often not realized by those who train.

So how does this happen? By trying to increase the pacing of the exercise (because you need to improve the time / increase the number of repetitions!). A person has the option to change the performance technique as they see fit. This is evident in beginners, especially those who have never engaged in a particular sport. For professionals (even former ones), the technical foundations are laid in muscle memory and the level of reflexes that they have accumulated which are not easily forgotten. That’s why gymnasts and ballerinas live with a flat back and perfect posture for the rest of their lives. These athletes can increase the pace of exercise by speed-strength and build biceps at home, without “compromising” the technique.
Consider the process and application of fitness science in a simple and well-known exercise called push-ups. Understanding such will require at least basic knowledge of anatomy and training theory.
Push-ups are the best forearm exercise one can do. It is aimed at improving muscle strength of both the hands and shoulder girdle. This means doing push-ups can give these muscles a fairly high load. Do this by following the static-dynamic mode where you start with slow movements. Doing so allows you to direct the main impact of the load on the contractile component (muscle tissue) and neutralize the elastic component of its connective tissue. But keep in mind that slow and controlled movement is much harder to perform.
In this case, the body must be held so that the load does not decrease, similar to the sumo squats exercise, it is performed where other muscles do not help to rise up, i.e. for push-ups, the back should maintain a straight and unchanged position. And movements must be performed only in the joints of the hands, and with full amplitude.
Intermediate position when doing push-ups: the whole body should maintain the same line as in the initial position.
The lowest position when performing push-ups: the whole body should maintain the same line as in the initial and intermediate positions.
When doing Crossfit, you will strive to increase the number of push-ups that you can perform, and increase the speed of their execution. This can be done without the application of technology which can result in the development of power capabilities. But this will take a lot of time. It is necessary to have someone help you track the progress and can give proper guidance (it is incredibly difficult to objectively evaluate yourself during the execution process).
How to do this as soon as possible, without waiting for the increase in power indicators? How can you increase the pace of a movement? The solution is very simple, and our body itself prompts it to us. It is important to facilitate the exercise, one example is by reducing the load. We change the appearance of push-ups: we lower the pelvis down to “squeeze” only the upper part of the body from the floor (directly the body). In this case, the feet, although they remain a reference point, cease to be the axis of rotation. The axis of rotation shifts to the hip joints, the shoulder strength decreases, the load decreases. In addition, such a position of the pelvis leads to the fact that when moving upwards inevitably there is an excession in the lower back. So, the body rises to a greater extent due to the tension of the extensor muscles of the spine, and not the muscles of the hands, although the visibility of movements in the elbow and shoulder joints remains.
Acceleration in execution is also often achieved through the use of an elastic component of muscles: we quickly lower ourselves “fall” down and sharply straighten our arms, “throwing” ourselves up. Connective tissue is involved in the movement, as a result of which the load on the contractile elements of the muscle (myofibrils) is reduced.
All these “tricks” can be used both simultaneously and separately. It depends mainly on the level of fitness and the degree of the equipment.
In fairness, it should be expected that such applications of technology in fitness are very common not only in Crossfit. In all types of fitness programs, trainees often find other ways to compensate for the lack of strength of the various muscle groups involved in a particular exercise.

In Crossfit, they are simply much more common, because the technique itself involves tracking the amount of exercise per unit of time. And in addition, a large number of repetitions (hundreds) are superimposed, which is less characteristic of other exercises. When the load falls on the muscles, it will tire from the repetitions, it will be a compromise in fitness technology and is almost inevitable.
The dangerous technical disturbances
Push-ups are primarily aimed at training muscles such as the triceps muscle of the shoulder, the clavicular (front) part of the deltoid muscle, and the clavicular part of the pectoralis major muscle.
In addition, the effect falls on the stabilizer muscles of various parts of the body:
- scapular stabilizers: rhomboid muscle, the middle part of the trapezius muscle, anterior dentate muscle
- stabilizers of the cervical spine: muscle straightening the spine (cervical), sternocleidomastoid muscle
- stabilizers of the lumbar spine: muscle, straightening the spine (lumbar), abdominal muscles.
Distortions of the technique will lead to the fact that the load is not on the muscles that the exercise was originally aimed at.
And the main danger of distortion of technique and transfer of load to other muscles is the risk of injury.
- When the technique is distorted, both the main working muscles and the muscles involved in the stabilization of various groups do not receive the target load. But, the load is redistributed to other muscle groups. If, for example, the head is released to the floor during push-ups (it is pushed forward), the neck stabilizers are turned off, and the neck flexors are excessively activated, moving the cervical spine forward, which leads to an increased load on the intervertebral discs of the cervical spine. This is the path to the gradual cumulative traumatization of the cervical spine, which is definitely not the initial goal of push-ups and a positive consequence of their effect on the body. Distortions of the technique lead to a change in the position of the bones in the joints, which, ultimately, can lead to chronic injury. Consider the lumbar spine. Bending in the lumbar spine during push-ups and excessive tension of the muscle straightening the spine can lead to compression of the intervertebral discs in the lumbar and this is fraught with well-known problems in the back.
- The transfer of the stabilization skill from one exercise to another is very important for everyday activities: the push-up technique affects how we “hold our back and stomach” in everyday life. If you do push-ups hundreds of times with over-flexed lumbar (which automatically means relaxed abdominal muscles, squeezed intervertebral discs, and intervertebral joints), this will gradually affect what posture you will use in everyday life with different positions and movements. A low back position will be a matter of course for you. This will increase the risk of getting a nerve pinched in the lumbar when trying to lift something off the floor, not necessarily even very heavy.
- Against the background of a large number of repetitions and fatigue, the likelihood of acute injury increases. Especially when performing high-amplitude movements. For example, cross-fitters have developed a very specific pull-up technique – using the inertia of rocking and “tossing” the body (the exact same logic works here – to pull yourself up many times in a row you have to find compromises, changing the technique, to “help” yourself accomplish your task by the number of repetitions ) And in this case, it’s very easy to “tear” your shoulder or elbow joint due to fatigue – especially if you force the load too quickly.
And one moment. We are committed to making good use of class time. Practically no one can do 300 push-ups in one training session with the correct technique, and when you try to do this, all the same, it takes a lot of time to complete. Therefore, we prefer to perform with clients, for example, 4 approaches of 15 push-ups (rather than several hundred), but so that the technique is perfect – no “imitating” movements, no redistribution of loads, and cunning “departures” from the load such as connecting inertia (“ tossing “of the body, sharp extension of the arms). It’s incredibly hard to keep the equipment tight, including psychologically. But the role of the coach is to control, assist, when necessary – to take part of the load so that the client “stretches” the movement correctly.
And in the free time, it is better to work out a larger number of muscle groups so that the training is more harmonious and versatile.
Attention: heart precautions
Another potential danger is an excessive burden on the cardiovascular system.
The exercise circles are performed with minimal rest pauses between them. The rest limit is determined by the options for constructing a workout, where it is necessary to either reduce the time to perform a certain number of exercises or increase their number in a given unit of time. Therefore, you will strive to squeeze the maximum out of yourself, including by reducing the intervals of rest.
At this speed and tension, the working muscles contract, mainly in anaerobic mode. After each exercise, rest is required to restore the working ability of the muscle groups involved in the movement. But in Crossfit, rest is supposed only after completing a circle in which exercises are performed without stopping, replacing each other. Moreover, most exercises in Crossfit are multi-joint (functional), requiring tension of a large number of large muscle groups to perform actions and stabilize positions. If after a circle you feel a lack of oxygen (breathing hard) and a frantic heartbeat, then this is a clear sign that you need rest to recover. If you reduce this rest and carry out circles further, trying to improve your quantitative and temporal indicators, can harm your heart.
At high continuous loads (with a heart rate above 90% of the maximum) for more than five minutes, the heart does not have time to increase the stroke volume, it has to increase the heart rate to supply the muscles with enough blood. The myocardium works at maximum, and the left ventricle does not have time to increase in size to pump more blood. Myocardial muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) contract with a high load, getting into the anaerobic energy supply mode. Some cardiomyocytes accumulate lactic acid, which destroys the cell. And this can cause a micro-heart attack, which often goes unnoticed (“a little heartache”). The flip side of this is the active growth of the myocardium (like in muscles). With foci of damage to some cells and limiting the extensibility of the heart. This phenomenon is often observed in professional athletes and is called the “athletic heart.” Its worst manifestation is sudden death during sports competitions, which, unfortunately, happens among football players, hockey players, and other athletes at a very young age and in the prime of life.
Our response to Crossfit
We are for safe training, with a clean, clear technique, and with optimal time costs. As an example, you can watch a video of the main part of the functional strength training, which we shot in one take with the participants of the gym workshop in Arkhangelsk. If you watch it all, or rather, train with us on the video, then make sure that you can “kill” and “stumble” on the simplest movements with minimal risk of injury. The only secret is to choose your own weight for the dumbbells – the heavier the dumbbell, the stronger the load. And here is the most important thing: you can get injured even with simple movements if the motion will be excessive for you personally. Proper weights (dumbbells) must be selected so that it is manageable.
Any methodology or training program will not bring the proper result if you neglect the issue of nutrition. In Crossfit, as in any other high-intensity power sport, the training athlete experiences enormous loads. Therefore, Crossfit nutrition should be carefully balanced to help the athlete recover the lost energy as quickly as possible.
Popular diets for Crossfit athletes
Nutrition for crossfitter, as well as for any other athlete, is one of the key factors affecting both the effectiveness of training and the health and well-being of the athlete as a whole.
Paleo diet
Usually, nutrition during Crossfit exercises is based on the paleo diet. The founder of Crossfit, Greg Glassman, urged all involved in cross-fitters to consume food to replenish the energy spent in training, but not to save it in the form of excess fat. In his opinion, it is the paleo diet that is capable of providing the crossfitter with energy for intensive training and all useful substances, but at the same time prevent the extra calories from being deposited “in reserve”.
Paleo dieting — only lean meats, vegetables, fruits, seeds, and nuts — is perhaps the most appropriate for a person living in the Paleolithic era, but for modern cross-fitters, such a strict approach to diet is sometimes not the most preferable. Professional cross-fitters rarely follow a paleo diet, due to its severe restrictions on carbohydrate intake.
Zone diet
The zonal diet is much more popular among crossfitters. This principle of Crossfit nutrition is based on the division of food portions by percentage: 40% carbohydrates, 30% protein, and 30% fat. It is recommended to eat every 4-5 hours.
The average daily diet of an athlete following a zonal diet is 1500-2000 calories. This allows us to consider this type of nutrition low-calorie. This diet, like the paleo, provides for a complete rejection of sugar. Nevertheless, useful complex carbohydrates ( oatmeal, barley, buckwheat ) are not only allowed, but also occupy an important place in the diet. Due to the ability to consume complex carbohydrates, the zonal diet can be considered more effective and preferable for recovery at high energy costs for CrossFit training.
CrossFit nutrition before and after training
There is a very careful attitude to the Crossfit nutrition system, which provides for strict control of the quality, composition, and quantity of foods used both before and after training. We have made for you a brief overview of what you can eat before and after training with weight loss and weight gain.
Features of nutrition before training
For a Crossfit athlete, nutrition before training plays almost the most important role in the daily diet. This meal provides an optimal supply of energy for productive physical activity. Given that Crossfit is a very energy-intensive and intense power sport, nutrition before such training should be as balanced as possible in terms of energy value and product quality.
As a general rule, eat food before training should be no later than 1.5-2 hours before exercise. In some cases, when the athlete’s metabolism is slowed down, eating before a workout should be 3-4 hours before it starts.
Foods recommended before exercise should be slowly digestible and not high in blood sugar. These products include cereals rich in useful complex carbohydrates, such as buckwheat, oatmeal, barley, and other cereals with a low glycemic index.
Please note that the use of protein and fat in combination with carbohydrates with a high glycemic index lead to a decrease in this index in carbohydrates.
Thus, the use of white bread in combination with butter or cheese does not cause such a sharp jump in blood sugar as the use of the same white bread, but without butter or cheese. This aspect should be considered when preparing a pre-workout menu.
Usually, a pre-workout meal should include complex carbohydrates, a large portion of the protein. Depending on the goal the athlete pursues in his training, the amount of protein can vary. For example, if the goal of training is to lose weight, then eating before exercise should include an increased amount of protein (about 20-30 grams). The amount of complex carbohydrates, on the contrary, is recommended to be reduced (15-20 grams). Fat before exercise for weight loss should generally be excluded.
If the goal of the training is to gain muscle mass, then in the pre-workout menu you can include not only an increased amount of protein (about 20-30 grams) but also a large portion of complex carbohydrates (50-60 grams), supplemented with a small amount of fat (no more than 3 -5 grams).
What to eat before training?
Here are a few options for eating before exercise:
- Whole grain bread with a piece of chicken or a piece of fish;
- Brown rice with a piece of lean fish or beef steak;
- Buckwheat with poached egg or a piece of chicken;
- Oatmeal with natural yogurt and omelet from 2-3 eggs;
- Barley with turkey (or chicken) and onions;
- Jacket potato with cheese and egg.
Whichever option you choose, it should be put in mind that eating food before a workout should not interfere with full-fledged exercises in the gym. Therefore, the most appropriate approach to nutrition before training is a full meal 2-3 hours before training. CrossFit nutrition also allows for a small snack. It can be done just before the start of physical activity – in 20-30 minutes.
Snacks before training
You can have a bite to eat before any workout using any of the following dishes:
- Natural yogurt with fresh berries and a teaspoon of oatmeal ;
- A cocktail of milk and fresh berries or fruits;
- Fresh fruit (banana, apple, pear);
- Low Fat Muesli Bar;
- Curd smoothie with banana and oatmeal in milk or natural yogurt.
The main rule of a pre-workout snack: a portion of food should be so small that the stomach was almost empty after 20-30 minutes by the start of the workout. And in the stomach, no heaviness could hamper intense Crossfit.
Post Workout Nutrition
Eating after a workout is one of the most important meals a Crossfit athlete has. Moreover, after active physical exertion, food is absorbed by the body much faster and more efficiently. Even simple carbohydrates will do good at this time – to restore energy reserves in the body. Professional athletes call this period a protein-carbohydrate or anabolic window. At this time, almost all food goes to restore energy and is included in the processes of anabolism.
As a general rule, after training, it is better to consume carbohydrates from high glycemic sources, that is, those carbohydrates that are absorbed very quickly and increase the level of insulin in the blood. After training, insulin is necessary for the athlete’s body to start the processes of anabolism (growth) and to prevent catabolism (destruction) of muscles.
Note: If after intense physical exertion, characteristic of Crossfit, the body does not receive a portion of fast carbohydrates, the catabolism process may start when the body begins to consume its own muscles to replenish energy.
It is extremely undesirable to allow this process to occur, so immediately after an intensive training session (after 5-10 minutes) it is recommended to take a small snack.
Snacks after training
It can be any of the following snack options:
- Milkshake with fresh fruits and berries;
- Natural yogurt with banana and strawberries;
- Low-fat curd cheese;
- Any sports bar;
- A pair of peanut butter sandwiches.
It should be remembered that Crossfit nutrition does not welcome the use of fast carbohydrates. Especially, it is extremely undesirable to do this in the evening, as well as if the athlete wants to lose weight. Therefore, if the training falls in the evening or at night, a small portion of cottage cheese (not more than 100-200 grams) with the addition of a couple of spoons of honey or half a banana is quite suitable for closing the protein-carbohydrate window.
After a snack and 1.5-2 hours of training, you can fully eat. A large portion of protein (about 40 grams) and complex carbohydrates (40-50 grams) should be included in the post-workout menu.
What to eat after training?
Dishes recommended for use after training:
- A portion of pasta made from durum flour with cheese and eggs;
- Beefsteak with jacket potatoes;
- Ragout of chicken, green beans and bell pepper with buckwheat;
- Wild rice with turkey;
- Oatmeal pancakes with cottage cheese.
However, there is an opinion that the appearance of a protein-carbohydrate window immediately after training is nothing more than a clever commercial move designed to increase sales of sports nutrition and drinks. And this version is confirmed in scientific circles. Researchers concluded that the start of anabolic processes in the body will not begin until the body recovers its energy potential of phosphates and ATP in the cells through oxidative processes.
It happens as follows. After intense strength training, a large amount of lactic acid is produced in the muscles, which, when it enters the blood, accumulates in the liver, where it is converted to glycogen. Resynthesis (reverse recovery) of glycogen is not possible without the participation of oxidative processes that provide the body with energy. Therefore, in the first 24-48 hours after intense training, the body is busy restoring and maintaining homeostasis, as well as converting lactic acid to glycogen through oxidative processes and is completely not interested in anabolism. So, in high doses of protein and carbohydrates, it is not needed at all.
Crossfit Sports Nutrition
Crossfit is inconceivable without high-quality and functional muscle mass and endurance. Therefore, in order to maintain strength and energy, in addition to a daily full-fledged diet, Crossfit nutrition fully allows the use of special sports nutrition.
The basic set of any novice crossfitter is a protein (or gainer, depending on the goals of training), BCAA amino acids, vitamin, and mineral complexes. Many athletes supplement this list at their discretion with creatine, chondro protectants, L-carnitine, various testosterone boosters, and other additives.
Proteins and gainers
Protein is a concentrated protein mixture that, when ingested with the help of special enzymes, is broken down into amino acids and spent on the building needs of the body. Protein in Crossfit, as a basic supplement, can be an excellent helper if there is no time or opportunity for a full meal.
A gainer is a protein-carbohydrate mixture, in which creatine, amino acids, or other trace elements are often added. Typically, such mixtures are used by people of a lean physique, who have no problems with excessive deposition of fat (ectomorphs), to quickly replenish the body’s energy potential after exercise and weight gain. With regard to Crossfit, as a highly energy-intensive and extremely intense power sport, the use of a gainer can be recommended before the training load to maintain a high intensity of training and good performance of the athlete. Weight gainers of modern production perfectly cope not only with the task of replenishing increased energy costs after Crossfit but also help muscles recover better after training.
Amino acids
Amino acids are the basis of all living things since it is from them that all the proteins of the body are composed. In sports nutrition, BCAA amino acids are most widely used. This complex of amino acids consists of three essential branched-chain amino acids: leucine, isoleucine, and valine. These amino acids makeup 35% of all amino acids in muscle tissue, activate the processes of anabolism, prevent catabolism, and contribute to a moderate fat-burning effect. The main difference between BCAAs and other amino acids is that they are not synthesized in the human body on their own, unlike the other 17 amino acids, so a person can only get them from food or sports supplements.
However, the need to consume BCAA amino acids is currently being questioned, as many researchers have concluded that athletes consume enough amino acids if they follow a balanced diet, including poultry, beef, pork, eggs, cheese, rich dairy products, and protein. It is these food products that are able to completely cover the body’s need for essential amino acids.
Vitamin and mineral complexes
Vitamin-mineral complexes are biologically active additives containing vitamins and minerals necessary to maintain all body functions. For cross-fitters, like any other athlete, vitamins and minerals play an important role in the processes of recovery, muscle gain, and weight loss. The modern market of vitamin-mineral complexes offers a wide range of prices for these supplements: from 200 rubles to 3000-5000 rubles. However, the effectiveness of a particular complex does not always depend directly on price. Often, athletes take vitamins by inertia, not knowing the actual needs of the body for a particular substance. Therefore, before taking this or that complex, it is advisable to undergo blood tests for vitamins. Hypervitaminosis (excess vitamin) is sometimes more dangerous.
The pattern of vitamin intake is usually 1-2 months of daily intake with a break of 2-3 months. It is not recommended to take vitamins throughout the year for the reason that the body may completely lose its ability to absorb vitamins, minerals, and other useful substances from food. Therefore, a break in taking even the most harmless vitamin-mineral complexes is necessary in any case.
Muscle Building Nutrition
On the issue of nutrition for building muscle mass at the moment, there are many different opinions and views, sometimes contradicting each other. Nevertheless, such a multivariate approach to the problem of gaining muscle mass can be explained only by the desire to bring something new, original, and unique to dietetics.
What to consider for the mass increase?
When gaining muscle mass, nutrition before exercise, along with nutrition after exercise, play the most important role. Therefore, not only the quality of nutrition but also the strict regimen of food intake is of particular importance. 2 hours before physical activity, a full meal should be carried out, consisting of a portion of complex carbohydrates (at least 50-60 grams) and high-quality protein (at least 20-30 grams). After a workout, you should immediately take a small snack (in this case, any milkshake with fruits is suitable, and a portion of the gainer from sports nutrition), and 1.5-2 hours after the workout, you need to have a full meal rich in complex carbohydrates and proteins, eating a small amount of fast carbohydrates for dessert is also acceptable.
Small and large, a set of muscle mass is built on the same principles, regardless of the athlete’s fitness level or other criteria.
Principles of Mass Gain
- The intake of junk food. In the case of muscle gain, the athlete’s daily diet should be 60-70% composed of high-calorie foods. Of course, you can’t beg the usefulness of eating fruits and vegetables, but with a diet aimed at gaining muscle, excess fiber will interfere with proper digestion and slow down the absorption of nutrients. Therefore, the proportion of fiber in the athlete’s diet in the case of muscle gain should not exceed 20-30%.
- 6 meals a day. 5 or 6 meals per day – the optimal number of meals with a set of muscle mass. With this type of nutrition, the digestive tract is not overloaded, and the amount of nutrients in the blood is always maintained at a certain level necessary for effective anabolism. Studies confirm the fact that if the amount of food calculated for 5-6 meals is eaten in 2 or 3 meals, then the excess nutrients will be stored in the form of fat and will not benefit the body. Moreover, it is proved that the anabolic effect of food intake lasts no more than 3-4 hours.
- Proportions of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. The daily diet for an athlete whose goal is to gain muscle mass should consist of 50-60% carbohydrates, 30-40% protein, and 15-20% healthy fat. In this case, you should use mainly complex carbohydrates. Most protein is recommended to be obtained from food, not from sports nutrition. The amount of fat is greatly reduced (below 10%) is highly not recommended in order to avoid metabolic disorders in the body.
By following these principles of nutrition, combining them with the right intense training, you can gain high-quality muscle mass.
Crossfit nutrition for weight loss
Many novice Crossfit athletes, especially girls, the dream of losing weight. Crossfit training itself is quite energy-consuming and, subject to dietary recommendations, contributes to proper and high-quality weight loss.
The main rule of losing weight is: consume less calories than you can spend them. Therefore, the correct diet for weight loss is the most important criterion for successful weight loss.
What to consider when losing weight?
When losing weight you should take into account a number of points.
- Local weight loss through nutrition does not happen —– this must be remembered. The human body consumes excess fat very competently, avoiding disproportionate burning of body fat. Usually, in the first place, a decrease in volumes is noticeable in the upper body (relevant for women), which may be taken by some women for its local burning, but this is not so. In fact, the processes of burning fat start immediately in the whole body, just the result is not always noticeable.
- Fast weight loss is the wrong weight loss. The result of rapid weight loss in the best case will be the loss of water by the body, in the worst – a significant loss of muscle mass and hormonal disorders. Usually, after quick weight loss, the excess weight returns in a short period of time with the effect of super-compensation and edema.
- Anyone can lose weight. It is enough to provide a lack of calories from food or increase their consumption through physical activity.
As in the case of a set of muscle mass, in the matter of losing weight, there are a number of principles, with which you can achieve lasting results.
The principles of losing weight in Crossfit
- Low-calorie food intake. The diet of an athlete who wants to lose weight should consist of 70-80% low-calorie foods. The most optimal and useful are fiber-rich foods that lead to fast saturation, have low-calorie content, and support the digestive tract. Fiber is also able to reduce the absorption of carbohydrates and fats from food, ensuring their gradual entry into the blood.
- 6 meals a day. As in the case of a set of muscle mass, when losing weight, you should eat often (at least 5-6 times a day) and in small portions. With this way of eating, the energy from food will be completely converted into energy to support vital functions, and its deficiency will be compensated for with the help of excess body fat. In addition, this diet allows you to minimize hunger during the day and prevents diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Exclusion of simple carbohydrates and restriction of fats. Simple (fast) carbohydrates, when ingested, cause a sharp increase in blood sugar, which provokes a feeling of hunger in 15-20 minutes. Moreover, simple carbohydrates have high-calorie content and are absorbed very quickly, provoking the production of insulin and starting the process of fat deposition. Fats also have high-calorie content and the body does not need to spend a lot of energy for their absorption.For example, if you eat carbohydrates per 100 calories, then 23 calories will be spent on processing and saving 77 calories from carbohydrates. But if you eat fats per 100 calories, then to save them you need only 3 calories, and 97 calories will remain in the body. Moreover, if you eat more fat than the body needs at the moment, the lipase enzyme is activated, which starts the process of fat deposition in adipocytes (fat cells). Nonetheless,
- Dietary restrictions before and after training. 2 hours before training, it is recommended to eat a small portion of protein. Immediately before the start of training, one should not eat, since the body must spend the energy of its own fat reserves, and not food. After training for 2 hours, it is recommended not to eat at all, since during this period the metabolic rate in the body increases sharply, and the concentration of fatty acids in the blood rises. If you eat immediately after training, then all the fatty acids will return back to adipocytes (fat cells), and if not, they will “burn out”.
Crossfit menu for the week
| Monday | |
| First meal: | 50 grams of oatmeal or a portion of oatmeal, one small banana or a couple of pieces of cheese, a glass of kefir or cocoa. |
| The second meal: | Three hard-boiled eggs or an omelet of three eggs, a small fruit (green apple or orange). |
| Third meal: | Low-fat beef steak (150 grams) with green beans , fresh vegetable salad with herbs, green tea or coffee without sugar. |
| Snack: | 30-40 grams of dried fruit or nuts, one medium-sized orange. |
| Fourth Meal: | 100 grams of white fish, vegetable salad with herbs and natural yogurt. |
| Snack before bedtime: | A glass (250 grams) of natural yogurt or kefir. |
| Tuesday | |
| First meal: | Three egg omelet or 50 grams of granola with bran, one small fruit (banana, apple or pear ), green tea or a glass of milk. |
| The second meal: | 100 grams of natural yogurt and a small portion of buckwheat porridge. |
| Third meal: | Chicken fillet (150 grams) with pasta from durum flour and cheese, some fresh sustanon250.pro vegetables. |
| Snack: | 50 grams of dried fruit or large fruit (banana, pear or apple). |
| Fourth Meal: | 150 grams of fish, casserole with vegetables, a portion of wild rice, a salad of fresh vegetables. |
| Snack before bedtime: | A glass of yogurt or 100 grams of cottage cheese. |
| Wednesday | |
| First meal: | Wheat or oatmeal, cocoa, a couple of pieces of cheese. |
| The second meal: | Two hard-boiled eggs, one small banana. |
| Third meal: | 150 grams of low-fat fish with buckwheat and green peas, a portion of fresh vegetable salad, a glass of kefir or milk. |
| Snack: | 100 grams of cottage cheese or a glass of natural yogurt. |
| Fourth Meal: | Turkey fillet (150 grams) with zucchini and eggplant, baked in the oven, vegetable salad with greens. |
| Snack before bedtime: | A glass of yogurt or milk. |
| Thursday | |
| First meal: | Three egg omelet with seafood or canned tuna, a slice of whole grain bread, cocoa or green tea. |
| The second meal: | A whole grain bread sandwich with cheese, a glass of milk. |
| Third meal: | Chicken fillet (150 grams) with mushrooms and onions, a serving of jacket potatoes, green tea. |
| Snack: | One banana or a handful of nuts (50 grams). |
| Fourth Meal: | White fish (150 grams) with buckwheat, a portion of vegetable salad with greens. |
| Snack before bedtime: | A glass of kefir or milk. |
| Friday | |
| First meal: | Buckwheat or oatmeal, a couple of pieces of cheese, cocoa. |
| The second meal: | A three-egg omelet or three hard-boiled eggs, a small fruit (apple or pear). |
| Third meal: | Beef or pork steak (5.2911 ounces) with pasta from durum flour, a portion of salad of fresh vegetables and herbs, green tea. |
| Snack: | A glass of natural yogurt or 100 grams of cottage cheese. |
| Fourth Meal: | Chicken fillet (100 grams) with green beans and bell pepper, a portion of vegetable salad. |
| Snack before bedtime: | A glass of yogurt or kefir. |
| Saturday | |
| First meal: | Three egg omelet with cheese and a slice of whole grain bread, cocoa. |
| The second meal: | Portion of millet porridge with pumpkin, green tea. |
| Third meal: | 150 grams of low-fat white fish with baked potatoes or wild rice, a portion of fresh vegetable salad, green tea. |
| Snack: | A glass of natural yogurt or 100 grams of cottage cheese. |
| Fourth Meal: | 150 grams of turkey fillet with green beans and buckwheat, a portion of fresh vegetables salad with herbs. |
| Snack before bedtime: | A glass of kefir or milk. |
| Sunday | |
| First meal: | Pearl barley or wheat porridge, a couple of pieces of cheese, cocoa. |
| The second meal: | Three hard-boiled eggs, one small fruit (apple, pear or orange). |
| Third meal: | 150 grams of turkey fillet with buckwheat or pasta from durum flour, a portion of a salad of fresh vegetables with herbs and natural yogurt. |
| Snack: | 50 grams of dried fruit or one small banana. |
| Fourth Meal: | 150 grams of red fish with jacket potatoes, a portion of fresh vegetable salad with herbs. |
| Snack before bedtime: | A glass of milk or natural yogurt. |
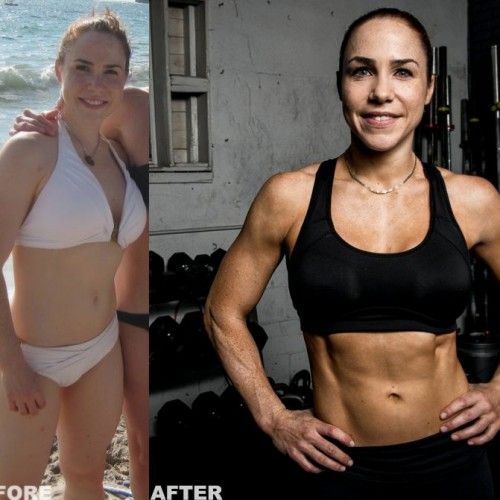
Crossfit transformation results
In the continuation of motivational articles devoted to the occupation of Crossfit, I bring to your attention to the stories of people who have changed the Crossfit.
1. Dusty Ashford

During my studies at school and college, I was in good physical shape, my height was 167 cm and weighing 70 kilograms. Riding a bicycle that kept me fit. One could say that I was thin. But then my daughter was born and I didn’t have time to do anything for about four years until she called me plump …
Once I was invited to a Crossfit class on the street. That moment was one of the most difficult in my life. I was introduced to burpi and kettlebell exercises. When we finished the WOD’s, everyone started making burgers, and I was lying near the flower bed for a long time. Crossfit kicked me in the ass so that I could work on myself.
Now I weigh 79 kilograms, which is definitely more than before, but it’s not just fat, but muscle mass, which I gained while doing a Crossfit.
2. Gerald Andres
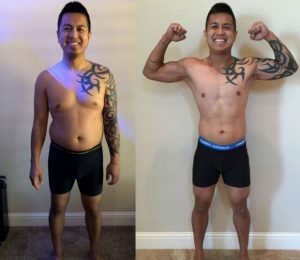
Before the Crossfit, I didn’t train much, to be honest, I practically didn’t train. However, my cousin was a big fan of Crossfit training and prompted me to take up this sport.
At first, I lost 9 kilograms after I gained 5 kilograms of muscles. I feel that my whole body and most of all my heart has become much stronger than it was before. In addition, I feel and look much better, and now I can actively play with my daughters
3. Mathew Waltz

For my full 22 years, I never took iron in my hands. I played football and all my workouts were mostly focused on endurance. All the time I thought that weight training should slow me down.
After entering college, I began to reduce my workouts to a minimum, add to this constant fast food, and my physical fitness began to leave much to be desired.
Now, after four years of Crossfit training, I can say that I am better than I could imagine. When I started to train, I thought, “How do these guys do it?” Now I myself can do exits by force, climbing a tightrope, walking on my hands, and much more.
4. Patrick Moen

After going to work, I fell ill. First, I thought that this was due to food poisoning or the stomach, in general, all the time in my treatment, I lost 18 kilograms. I did not have any physical activity at the time and lost my weight.
As soon as I recovered, I began to engage by doing Crossfit. The first is 2 times a week, and after going 4-5 times a week, I can proudly say that I have regained all my weight and even gained a little muscle. In fact, I am now in better shape than I have ever been.
Other compilation of the Crossfit transformation:










